Abstract
Introduction: Lymphomatoid granulomatosis (LyG) is a rare EBV associated B cell lymphoproliferative disorder with unique histopathologic features (angiocentric and angiodestructive lesions), heterogeneous disease course and variable response to different therapies. Few reports have ever been published, and many patients have a poor prognosis. In this study, we present the largest single center experience on the characteristics, management and the outcomes in patients (pts) with LyG according to current WHO classification system.
Methods: This is an analysis of 19 pts with confirmed diagnosis of LyG evaluated at MDACC between 1994 and 2014. Following IRB approval, pts were identified from the institutional database and data was collected on the clinico-pathological features, treatments and clinical outcomes following therapy. Histopathological and immunohistochemistry data was collected on available cases. Progression free (PFS) and overall survival (OS) was defined from the time of initial diagnosis to treatment failure or death.
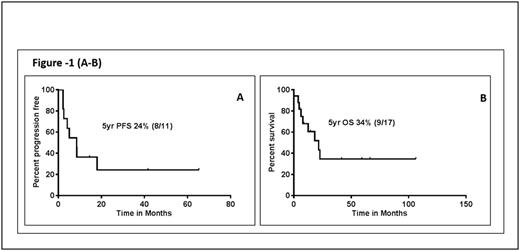
Results: Median age was 56 years (range, 19 to 90) and 53% were males. Among the pts with available data, performance status was ≥1 in 12/14 (85%) pts, B symptoms were observed in 6/14 (43%) pts, and 100% pts had stage 4 disease, including nodal involvement 2/19 pts (10%). Extranodal involvement (with/without concordant involvement of other sites) was observed in all pts. The lung was the most common site of involvement (78%), followed by central nervous system (28%), skin (22%) and liver (17%). Mediastinal, adrenal, renal, breast and abdomino-pelvic involvement was rare. Two pts had marrow involvement at initial presentation. Chronic lymphocytic inflammation with pontine perivascular enhancement responsive to steroids (CLIPPERS) was noted in one patient 2 years prior to the diagnosis. Seven pts had a pre-existing cancer or a medical condition associated with immunosuppression (one patient with chronic myeloid leukemia, one chronic lymphocytic leukemia, one myelodysplastic syndrome, one with hypereosinophillic syndrome, one prostate cancer and 2 pts were on immunosuppressive therapy). One pt developed Hodgkin's lymphoma after the diagnosis. At baseline; anemia (Hb <11 g/dL) was seen in 46%, thrombocytopenia (platelet count <100 K/μL) and leucocytopenia (WBC <3 K/μL) was seen in 15% each. LDH > upper limit of normal was observed in 33% pts. PET-CT scan was performed in 7 pts, and was positive in 100%. Histopathologic studies showed that LyG grading was available in 10 pts of which 3 (30%) were grade 2 and 7 (70%) were grade 3. Immunohistochemically, CD20 was positive in 100%, CD30 in 100%, the median Ki-67% was 55% (range 20-70), and EBV-positive cells were noted by in situ hybridization in in 89% pts. In the 11 pts with treatment information, 4 received R-CHOP, 2 received R-EPOCH, 2 received rituximab alone, and 1 each received methotrexate and CHOP. Overall response to treatment was 55%, including complete remission in 36%. (3/4 pts achieved CR following R-CHOP). With a median follow up of 60 months, median progression free survival (after initial therapy) was 8.5 months. Median overall survival was 22 months (Figure-1 (A-B). Four patients died due to disease progression, 3 from unknown causes and 2 due to sepsis and pneumonia respectively.
Conclusions: LyG remains a diagnostic and a therapeutic challenge to hematopathologists and clinicians. Although responses have been observed following rituximab containing combination therapy, most patients relapse and the optimal treatment strategy remains unknown. The rarity of the disease and lack of molecular data in LyG are major limiting factors to developing targeted approaches, and further studies interrogating the genomic landscape in LyG are ongoing at our institution. The high rates of CD20 and CD30 expression suggest targeted therapy may be of benefit, but require prospective study. Multicenter collaboration is needed to further develop successful approaches to study and treat this rare disease.
Nastoupil: Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Abbvie: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Genentech: Honoraria, Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Honoraria, Research Funding; Gilead: Honoraria; Karus Therapeutics: Research Funding. Neelapu: Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Kite Pharma: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Karus: Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Merck: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Cellectis Inc.: Research Funding; Poseida Therapeutics, Inc: Research Funding. Westin: Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Apotex: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Kite Pharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Wang: Acerta Pharma: Consultancy, Research Funding; BeiGene: Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Dava Oncology: Honoraria; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; June Therapeutics: Research Funding; Kite Pharma: Research Funding; Onyx: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; Proteolix: Honoraria, Research Funding; Asana Biosciences: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal